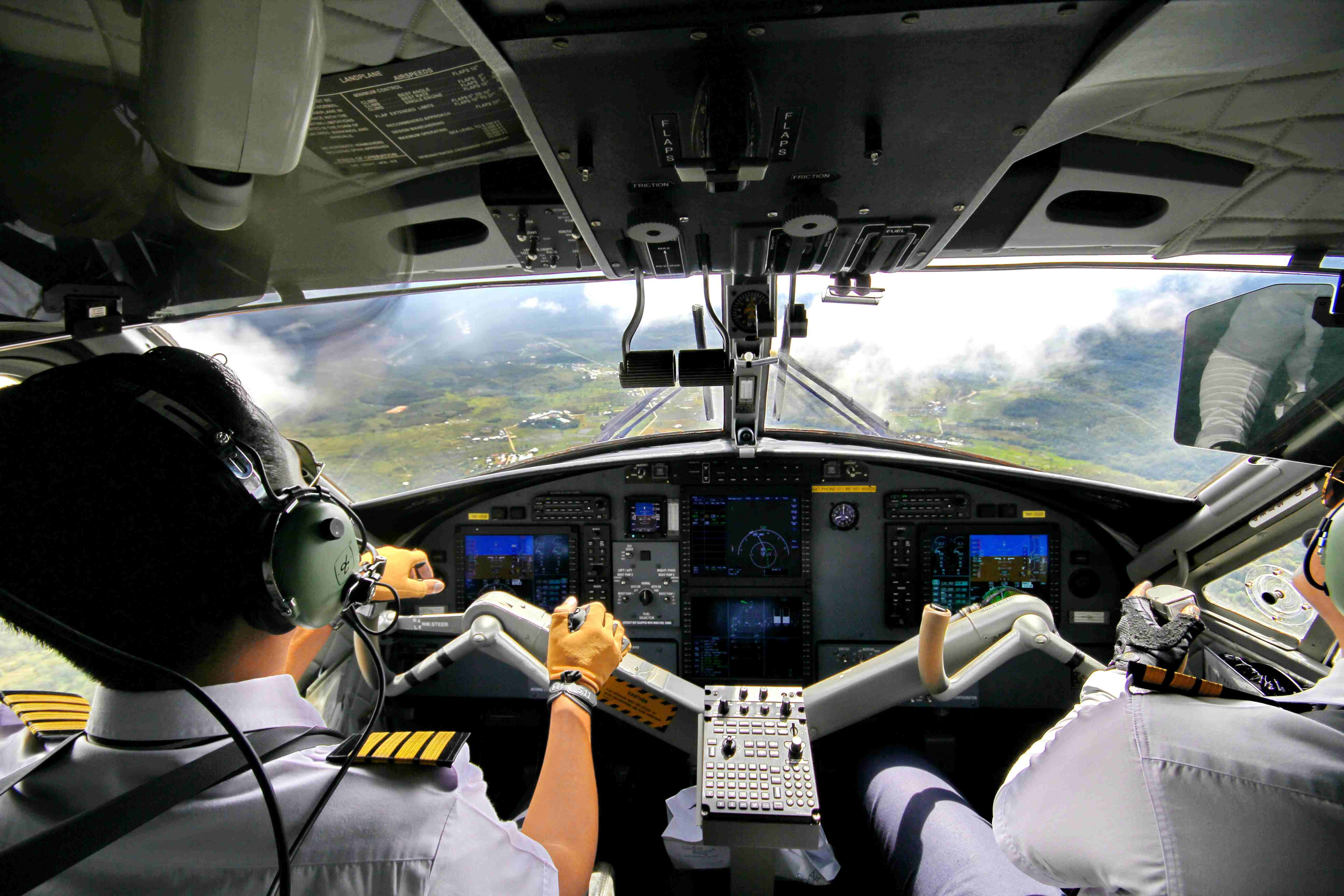
1. **History of Pilot Training in the United States**
In the United States, the history of pilot training can be traced back to the early 20th century when aviation was still in its infancy. The need for trained pilots became increasingly evident as the field of aviation rapidly evolved.
1.1 **Early Beginnings**
– The Wright brothers, Orville and Wilbur Wright, are renowned for achieving the first controlled, sustained flight in 1903. Their groundbreaking accomplishment sparked the interest and development of aviation in the United States.
– As aviation technology progressed, the military recognized the strategic importance of aircraft and the need for skilled pilots to operate them effectively.
1.2 **World War I and Aviation Training**
– The United States entered World War I in 1917, and the demand for trained pilots soared. The U.S. Army Air Service established flight training schools to prepare pilots for combat.
– Training programs focused on honing pilots’ skills in aerial combat, navigation, and aircraft maintenance to ensure readiness for the battlefield.
1.3 **Establishment of Civilian Flight Schools**
– Following World War I, there was a surplus of military pilots with valuable flight experience. Many of these pilots transitioned into civilian life and sought opportunities to share their aviation knowledge.
– Civilian flight schools began to emerge across the country, offering aspiring pilots the chance to learn how to fly under the guidance of experienced instructors.
1.4 **Expansion of Commercial Aviation**
– The post-World War I era saw a rise in commercial aviation as passenger air travel gained popularity. Airlines recognized the need for well-trained pilots to operate their aircraft safely and efficiently.
– Flight training programs evolved to meet the growing demand for commercial pilots, emphasizing skills such as commercial pilot licensing, instrument flying, and multi-engine operations.
1.5 **Modern Era of Pilot Training**
– In the 21st century, pilot training in the United States continues to evolve in response to advancements in aviation technology and changing regulatory requirements.
– Today, aspiring pilots can choose from a variety of flight training programs offered by accredited institutions, flight academies, and universities to pursue careers in both commercial and general aviation.
1.6 **Regulatory Oversight**
– The Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) plays a crucial role in regulating pilot training standards and ensuring the safety of the national airspace system.
– Flight schools and training organizations must adhere to FAA regulations and guidelines to maintain the quality and integrity of pilot training programs.
Overall, the history of pilot training in the United States reflects a rich legacy of innovation, adaptability, and commitment to excellence in preparing pilots for the challenges and opportunities of aviation.

2. Top Pilot Institutes in America
When it comes to pursuing a career in aviation, choosing the right pilot institute is crucial. In America, there are several prestigious institutions known for providing top-notch training and education to aspiring pilots. Here is a list of some of the top pilot institutes in America:
1. United States Air Force Academy (USAFA)
– The United States Air Force Academy, located in Colorado Springs, Colorado, is renowned for its rigorous training programs and emphasis on leadership development. Graduates from USAFA often go on to become highly skilled pilots in the U.S. Air Force.
2. Embry-Riddle Aeronautical University
– Embry-Riddle Aeronautical University, with campuses in Daytona Beach, Florida, and Prescott, Arizona, is a world leader in aviation and aerospace education. The university offers a wide range of programs in pilot training, aeronautical science, and aviation management.
3. Purdue University
– Purdue University, located in West Lafayette, Indiana, offers a top-tier aviation program through its School of Aeronautics and Astronautics. The university has state-of-the-art facilities and experienced faculty members who provide students with comprehensive training in aviation.
4. University of North Dakota
– The University of North Dakota is home to one of the most respected aviation programs in the country. With a strong focus on hands-on training and real-world experience, UND prepares students to excel in various aviation-related careers, including piloting.
5. Ohio State University
– Ohio State University’s Center for Aviation Studies provides students with a unique learning experience in the field of aviation. The university offers programs in professional pilot training, aviation management, and air transportation, preparing students for successful careers in the aviation industry.
6. Western Michigan University
– Western Michigan University’s College of Aviation is known for its comprehensive pilot training programs and cutting-edge facilities. The college offers a variety of aviation-related degrees and certifications, equipping students with the skills and knowledge needed to excel in the aviation field.
7. Kansas State University
– Kansas State University’s Polytechnic Campus in Salina, Kansas, is home to the prestigious Aviation Program. The university provides students with hands-on training, advanced flight simulator technology, and industry connections that help students kickstart their careers in aviation.
Choosing a pilot institute is a significant decision that can shape your future as a professional pilot. Consider factors such as program offerings, faculty expertise, industry partnerships, and alumni success when selecting the right institute for your aviation education. These top pilot institutes in America are renowned for their excellence in training and preparing the next generation of skilled pilots.

### 3. Requirements for Enrolling in a Pilot Institute
Becoming a pilot is a prestigious and rewarding career choice that requires commitment, dedication, and meeting specific requirements. If you are considering enrolling in a pilot institute in America, here are some common requirements you should keep in mind:
1. **Education Background**:
– Most pilot institutes require aspiring students to hold a high school diploma or GED equivalent.
– Some institutes may have specific requirements related to the grades achieved in subjects such as mathematics, physics, and English.
2. **Age Limit**:
– Generally, the minimum age requirement for enrolling in a pilot institute is 18 years old.
– However, some institutes may permit enrollment at a younger age with parental consent.
3. **Health and Medical Fitness**:
– Aspiring pilots must meet specific medical standards set by the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) to ensure they are physically fit to operate an aircraft.
– This typically involves obtaining a medical certificate from an FAA-approved Aviation Medical Examiner.
4. **Language Proficiency**:
– Proficiency in English is crucial for effective communication in aviation.
– Some pilot institutes may require candidates to demonstrate English language proficiency through standardized tests like the International English Language Testing System (IELTS) or the Test of English as a Foreign Language (TOEFL).
5. **Financial Resources**:
– Pursuing pilot training can be a significant financial investment. Applicants need to consider the tuition fees, training materials, living expenses, and potential costs associated with obtaining licenses and ratings.
– Some pilot institutes offer financial aid, scholarships, or payment plans to assist students in managing the costs.
6. **Security Clearances**:
– In some cases, aspiring pilots may be required to undergo background checks and obtain security clearances to work in certain aviation sectors, such as commercial or military aviation.
7. **Other Requirements**:
– Additional requirements may vary depending on the specific pilot institute and the type of training program being pursued.
– These may include passing entrance exams, aptitude tests, interviews, and possibly completing a certain number of hours of flight experience.
Before applying to a pilot institute in America, it is essential to thoroughly research the specific requirements of the institute of interest to ensure that you meet all prerequisites for enrollment. Meeting these requirements will set you on the right path towards achieving your dream of becoming a pilot.
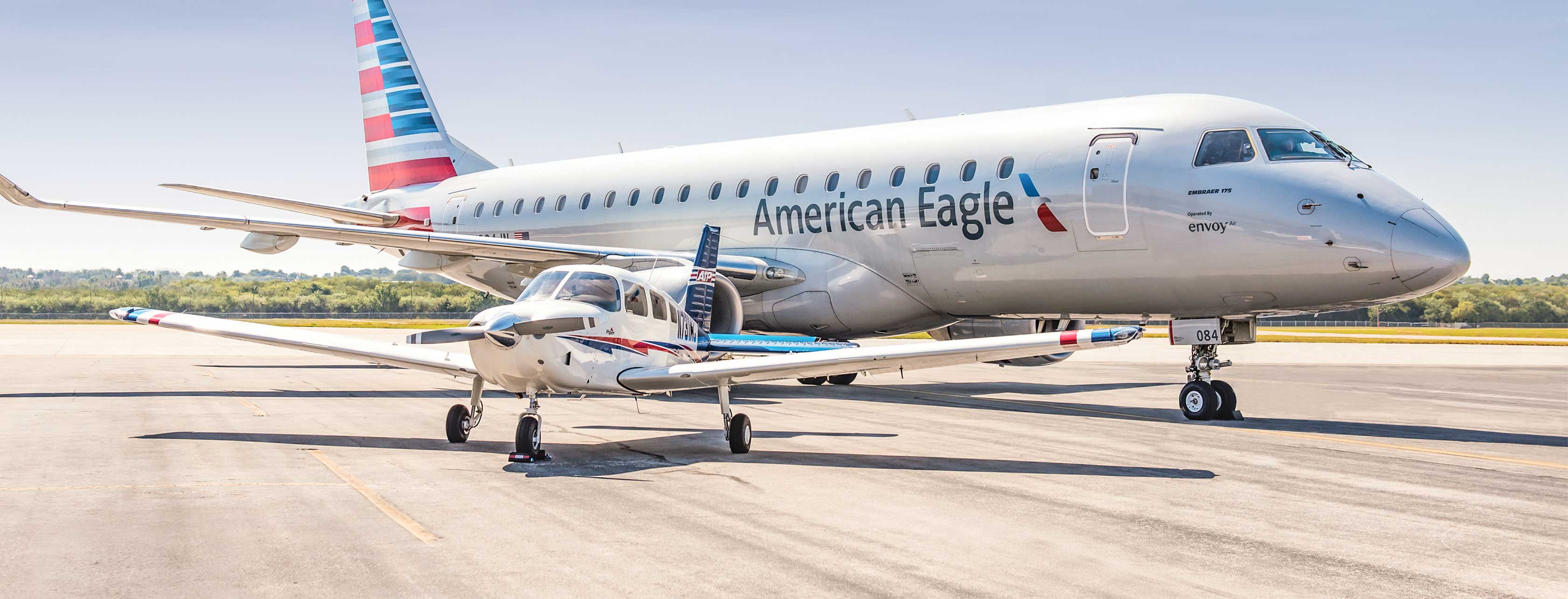

4. Career Opportunities for Graduates of Pilot Institutes
Graduates of pilot institutes in America have a wide array of career opportunities available to them in the aviation industry. These institutes provide comprehensive training and education that prepare individuals for successful careers as professional pilots. Below are some of the career paths that graduates can pursue:
1. Airline Pilot:
One of the most common career paths for graduates of pilot institutes is becoming an airline pilot. Airline pilots are responsible for flying passengers or cargo to various destinations around the world. They work for commercial airlines and are required to have extensive training and experience in order to safely operate large commercial aircraft.
2. Charter Pilot:
Graduates can find opportunities as charter pilots, flying customers to specific destinations on demand. Charter pilots may work for private companies, individuals, or charter airlines. This role offers the opportunity to fly a variety of aircraft and visit different locations based on clients’ needs.
3. Flight Instructor:
Becoming a flight instructor is another popular career choice for graduates of pilot institutes. Flight instructors are responsible for teaching and training aspiring pilots to obtain their licenses and certifications. This role requires strong communication skills, in-depth knowledge of aviation principles, and the ability to provide clear and effective instruction.
4. Corporate Pilot:
Graduates may also pursue a career as a corporate pilot, flying private aircraft for corporations or high-net-worth individuals. Corporate pilots are responsible for transporting executives, employees, and clients to various business meetings and events. This role often involves operating smaller, business jets and maintaining high levels of discretion and professionalism.
5. Air Ambulance Pilot:
Another rewarding career option for graduates is becoming an air ambulance pilot. Air ambulance pilots transport critically ill or injured patients to hospitals or medical facilities in a timely and safe manner. This role requires quick decision-making skills, strong situational awareness, and the ability to work effectively in high-pressure situations.
6. Cargo Pilot:
Graduates can also explore opportunities as cargo pilots, transporting goods and packages to domestic and international destinations. Cargo pilots work for cargo airlines or freight companies and are responsible for loading, unloading, and safely delivering various types of cargo. This role often involves flying overnight or long-haul flights and requires strong logistical and organizational skills.
Overall, graduates of pilot institutes in America have a diverse range of career opportunities available to them in the aviation industry. Whether aspiring to become an airline pilot, flight instructor, charter pilot, or pursue other specialized roles, the training and education provided by pilot institutes equip individuals with the skills and knowledge needed to succeed in their chosen career path.

5. Challenges and Trends in the Pilot Training Industry in America
In recent years, the pilot training industry in America has undergone significant challenges and transformations influenced by various factors. This subsection explores some of the key challenges and emerging trends shaping the landscape of pilot training in America:
5.1. Shortage of Qualified Instructors: One of the prominent challenges facing the pilot training industry in America is the shortage of qualified flight instructors. As the demand for trained pilots continues to rise, the industry is grappling with a lack of experienced instructors to impart knowledge and skills to aspiring pilots. This shortage not only hampers the quality of training but also leads to delays in pilot certification and an overall bottleneck in the training pipeline.
5.2. Technological Advancements: The pilot training industry in America is witnessing a rapid integration of advanced technologies into training programs. From flight simulators to computer-based training modules, technology is revolutionizing the way pilots are trained. However, keeping up with the latest advancements and ensuring that training programs are aligned with industry standards pose challenges for pilot institutes.
5.3. Regulatory Frameworks and Compliance: The aviation industry is highly regulated, and pilot training institutes in America have to adhere to stringent regulatory frameworks set forth by the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) and other governing bodies. Ensuring compliance with evolving regulations, updating training materials accordingly, and maintaining certification standards can be challenging for pilot training institutes.
5.4. Diversity and Inclusion: With the aim of fostering diversity and inclusion within the aviation industry, there is a growing emphasis on providing equal opportunities for individuals from different backgrounds to pursue a career as a pilot. Pilot institutes in America are faced with the challenge of creating inclusive training environments and programs that cater to a diverse pool of aspiring pilots.
5.5. Industry Partnerships and Collaboration: To meet the demands of a dynamic aviation industry, pilot training institutes in America are increasingly forming partnerships with airlines, aircraft manufacturers, and other industry stakeholders. Collaborations help in aligning training programs with industry requirements, providing access to state-of-the-art resources, and enhancing job placement opportunities for graduates.
5.6. Sustainable Practices and Environmental Concerns: As the aviation industry moves towards sustainability and reduced environmental impact, pilot training institutes are under pressure to incorporate eco-friendly practices into their training programs. From promoting fuel-efficient flying techniques to integrating sustainability modules into the curriculum, pilot institutes are adapting to the evolving environmental trends in the industry.
5.7. Virtual Training and Remote Learning: The emergence of virtual training tools and remote learning platforms has introduced a new dimension to pilot training in America. With advancements in virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) technologies, pilot institutes are exploring the feasibility of integrating virtual training modules into their programs to enhance the learning experience and offer greater flexibility to students.
Overall, the pilot training industry in America is navigating through a period of change marked by both challenges and progressive trends. Adapting to technological advancements, regulatory requirements, and industry shifts is essential for pilot institutes to equip future generations of pilots with the skills and expertise needed to excel in the dynamic aviation sector.